Appendicitis In Kids and Teens
What Is Appendicitis?
Appendicitis is when the appendix gets blocked and becomes infected.
The appendix is a small organ attached to the large intestine in the lower right side of the belly.
Appendicitis is an emergency. It’s important to know what to look for and get medical care right away.
What Causes Appendicitis?
When the appendix gets blocked, too much bacteria can grow and cause an infection. Some of the things that might block the appendix are:
- hard, rock-like stool (poop)
- swollen lymph nodes in the intestines
- parasites and other infections
Appendicitis is not contagious. Kids can’t catch it from someone who has it.
What Are the Signs & Symptoms of Appendicitis?
The first signs of appendicitis are often a mild fever and pain around the belly button. It might seem like just a stomachache. But with appendicitis, the pain usually gets worse and moves to the lower right side of the belly.
If your child has belly pain, be on the lookout for these signs of appendicitis:
- strong pain, mainly around the belly button or in the lower right part of the belly (the pain might come and go at first, then grow steady and intense)
- low-grade fever
- loss of appetite
- nausea (feeling sick) and vomiting (throwing up)
- diarrhea (especially small amounts, with mucus)
- swollen belly
If pain spreads across the belly, it may mean the appendix has burst. Doctors call this ruptured appendicitis, and it’s serious. A high fever reaching 104°F (40°C) is another sign of a burst appendix.
Call your doctor right away if you think your child has appendicitis. The sooner it’s caught, the easier it will be to treat.
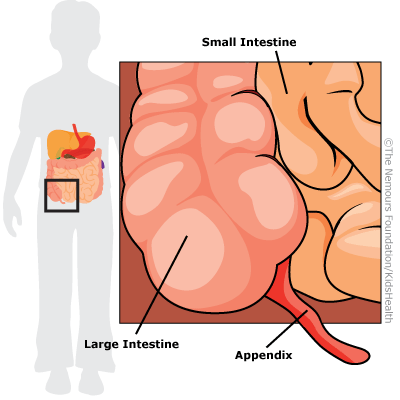
What Problems Can Happen With Appendicitis?
If an infected appendix isn’t removed, it has the potential to burst about 48 to 72 hours after symptoms first start. This can spread
bacteria
inside the body. The infection might form a large collection of pus (an abscess) or spread throughout the belly.
Who Gets Appendicitis?
Appendicitis mostly affects kids and teens between 5 and 20 years old. It is rare in infants.
How Is Appendicitis Diagnosed?
The symptoms of appendicitis can be a lot like those of other medical problems (like kidney stones, pneumonia, or a urinary tract infection). So it can be a challenge for doctors to diagnose.
To find out if a child has appendicitis, a doctor will examine the belly for signs of pain and tenderness. The doctor will order blood tests and urine tests. Some kids also get an X-ray of the abdomen and chest, an ultrasound, or a CAT scan.
The medical team may tell you not to give your child any food or drink. This is in case your child needs surgery.
How Is Appendicitis Treated?
A surgeon will operate to take out the infected appendix. This is called an appendectomy. Most of the time, surgeons use a small device called a laparoscope to remove the appendix through a small cut on the belly. Kids who get this surgery usually stay in the hospital for a day.
The care team may give your child intravenous (IV) fluids and antibiotics before and after surgery. This helps prevent problems such as an infection. Kids get pain medicine if they need it.
A child who had a burst appendix might need to stay in the hospital longer after an appendectomy. That gives the antibiotics time to kill any bacteria that spread into the body.
Can Appendicitis Be Prevented?
There is no way to prevent appendicitis. But when kids get the right medical care quickly, doctors usually find and treat it without problems.
