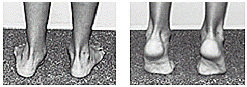
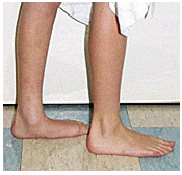
Children usually have low arches because they are loose-jointed. The arch flattens when they stand.

One in seven children never develop an arch.
However, one in seven children never develop an arch. Should he or she have special shoes? The natural history of most flexible flatfoot conditions is to slowly improve over time. The arch develops whether the child wears special shoes or goes barefoot. So special wedges, inserts, or heels are not necessary for the normal toddler who has flexible flatfeet. Parents worry about flatfoot, but some degree of flatfoot is normal in infants and early childhood.
Examination
The doctor will want to be certain that your child has the typical form of flexible flatfoot that improves over time without treatment (in rare cases a flatfoot is stiff and will not follow the normal course of slow self correction).
Imaging
X-rays are commonly ordered to assess flatfoot severity.
Treatment
Just as normal children are different heights, different arches have different heights. Wearing a pad under the arch of a simple hyper-mobile flatfoot may make the child less comfortable, and wastes money.
Summary
Flatfoot in children are a normal variation related to slight laxity of ligaments. The condition improves over time and research has shown that corrective shoes and inserts do not help to correct flatfoot (see reference below). The condition slowly improves over time, whether or not it is treated. Accordingly, the scientific approach to flatfoot treatment is to not use expensive shoes or inserts. Instead comfortable normal shoes or going barefooted is appropriate, with the child being followed to monitor correction over time.